Islam
An Apologist’s Insights on “God’s Not Dead”
 I recently had the chance to watch “God’s Not Dead,” a film which presents a story in which a college student decides to take a stand for his faith against the pressure of an atheistic philosophy professor. A summary of the plot may be found here. As an apologist with an MA in the field, I thought my comments might help provide some insight into the film. I’ll offer a look at some aspects of the film which I wanted to address. Feel free to chime in in the comments with your own thoughts.
I recently had the chance to watch “God’s Not Dead,” a film which presents a story in which a college student decides to take a stand for his faith against the pressure of an atheistic philosophy professor. A summary of the plot may be found here. As an apologist with an MA in the field, I thought my comments might help provide some insight into the film. I’ll offer a look at some aspects of the film which I wanted to address. Feel free to chime in in the comments with your own thoughts.
Apologetics
The movie presents a clear picture of the need for apologetics. When challenged by attacks on the faith it is important to always have a reason for the hope within (1 Peter 3:15). Josh Wheaton–the protagonist–put together a decent presentation of various evidences for theism in the snippets that viewers get through the film. Of course, these are very simplified and don’t address several major issues with the arguments, but it gets the point across. It also, I have noted through conversations with others, spurred much interest in the area of apologetics. That’s awesome!
That said, I think there are some issues with even the arguments presented in the film. First, after Wheaton has presented the cosmological, design, and other arguments for theism, he is challenged by Professor Radisson on the notion that one just has to choose between atheism and theism. Wheaton acknowledges that yes, it is a choice. Now, there are a number of issues with this portrayal. First, it treats the balance of evidence as a kind of 50/50 proposition, which is, I would think, hardly the position of anyone. Second, it presents a view of belief in which we can just choose what we believe. This is called “doxastic voluntarism” which is a fancy way of saying that one can believe propositions at will. But that is a highly controversial position (just try to force yourself to believe that “Fairies fill my refrigerator every morning” and you’ll see the folly of it) and also flies in the face of biblical accounts of what faith is. Third, here I’ll tip my bias a bit and say I’m fairly well convinced that the balance of evidence is hardly 50/50 but actually compelling.
Another difficulty with the apologetic in the film is that it seems like the lynchpin argument offered was actually just a point of rhetoric. Wheaton presses Professor Radisson and asks “Why do you hate God?” and follows it up with [paraphrased]: “How can you hate someone who doesn’t exist?” This is the last straw and what prompts the class to vote by standing to say that “God’s not dead.” Although I think rhetoric has a clear place in the Christian apologetic (and has since the earliest times: see the apologetic works of Lactantius and Arnobius in the 200-300s AD), I thought it was an odd choice to make it the climactic argument for God. Perhaps it was because this added to the drama of the moment–and I suspect that’s right–but it did so at the cost of detracting from whatever apologetic the film could put forward.
I did, however, appreciate the interaction with some top scholars like Hawking and Lennox. I think it is very important for Christians interested in apologetics to read the top scholars in their fields in order to best get acquainted to the arguments.
Characters or Caricatures?
The way the Muslim father was portrayed was problematic. In the beginning of the film we see him dropping off his daughter and showing great concern for her. Later, he shares an intimate discussion of his faith and the importance of obedience in his background. But then, when it is revealed his daughter has converted to Christianity, he not only kicks her out of the house, but he also immediately hits her more than once. Now, I make no claims to being an expert on this, but I know from anecdotal evidence only that people are indeed kicked out of their homes for converting to Christianity (and sometimes for deconverting), and this is surely a bad thing. It’s not a bad thing to address this as an issue.
But the problem I saw was that the Muslim father’s immediate reaction was violence, without any explanation or any background for thinking this would be a reaction. The rest of the film up to this point had shown him as a caring father who was concerned for the faith and well-being of his daughter. To have him immediately turn to violence when she converted was jarring and I think it speaks to our cultural presuppositions about the religious “Other” to portray the “Other”–the Muslim–in that way. We need to move beyond such stereotypes and into genuine dialogue with those of other faiths, always looking to share the light and love of Christ with them.
On the positive side, the film did do a great job speaking to the importance of reaching out to others like the young man from China. It also emphasized missions in a number of ways, like centering some major plot points around a very amiable character as a missionary.
Pastoral Care
I appreciated the comments about the work of a pastor, in which Pastor Dave in the film was comparing his own work to that of a missionary friend’s and felt his own day-to-day tasks were mundane and trivial. The answer given by the missionary, however, was essentially that such work is part of the work of God as well and that we each occupy a place which God has put us in to make an impact on the world. I thought this was a great message and one that deserves further exploration.
On the other hand, I thought that the pastoral care at points in the movie presented some difficulties. For example, Pastor Dave’s conversation with Josh Wheaton before Wheaton decides to for sure stand up to his professor boiled down to a couple citations (not even quotations) of Bible verses to look up later and the comment that “It’s not easy, but it’s simple” [I may have the order in this quotation wrong]. I’ll be blunt: I think that this is actually a gross oversimplification. Quoting Matthew 10:33 (click for reference) does not actually make the issue facing Wheaton “simple.”
For example, would it be “denying” Christ to acknowledge that one might not have the resources available as a freshman student in a general studies philosophy class (and not a major) to take on a philosophy professor on the topic of God’s existence? I don’t think so. One could instead acknowledge that both the clearly adversarial tone taken in the environment and one’s own lack of knowledge or expertise in the area make it likely that one may actually harm the body of Christ by, well, looking like a freshman non-philosophy student outmatched by an atheistic philosophy professor. Wheaton, of course, has the benefits of film, so he is able to put together a beautiful powerpoint each week and manages to pound the books so hard that he can articulate the cosmological, design, and other arguments within a few days. But is this a realistic perspective? Moreover, is it a “simple” application of the passage to our lives?
Conclusion
“God’s Not Dead” awakens people to the need for apologetics. That is a great compliment, because it is a much-needed awakening. However, it has several issues (including those mentioned above) with the presentation of apologetics, its portrayal of the “Other,” and the oversimplification of several arguments, positions, and even pastoral care and reading of texts. In short, it’s a mixed bag.
Links
Be sure to check out the page for this site on Facebook and Twitter for discussion of posts, links to other pages of interest, random talk about theology/philosophy/apologetics/movies and more!
SDG.
——
The preceding post is the property of J.W. Wartick (apart from quotations, which are the property of their respective owners, and works of art as credited; images are often freely available to the public and J.W. Wartick makes no claims of owning rights to the images unless he makes that explicit) and should not be reproduced in part or in whole without the expressed consent of the author. All content on this site is the property of J.W. Wartick and is made available for individual and personal usage. If you cite from these documents, whether for personal or professional purposes, please give appropriate citation with both the name of the author (J.W. Wartick) and a link to the original URL. If you’d like to repost a post, you may do so, provided you show less than half of the original post on your own site and link to the original post for the rest. You must also appropriately cite the post as noted above. This blog is protected by Creative Commons licensing. By viewing any part of this site, you are agreeing to this usage policy.
Really Recommended Posts 10/11/13- Worldview, Wilberforce, and World [Religions]! Plus some more!
 Dear readers, this week I stumbled across a collection of posts I had prepared some months ago for your reading, but had forgotten to actually share! I have now rectified that error by placing the following posts before you for your reading pleasure. Check ’em out, and as always, leave a comment to let me know what you thought!
Dear readers, this week I stumbled across a collection of posts I had prepared some months ago for your reading, but had forgotten to actually share! I have now rectified that error by placing the following posts before you for your reading pleasure. Check ’em out, and as always, leave a comment to let me know what you thought!
Dallas Willard – The Nature and Necessity of Worldviews (Video)– An hour-long presentation by the late Dallas Willard on worldviews. He provides some good insights into what makes up a worldview and the applications thereof.
William Wilberforce, Hannah More, and Their Legacy in Public Education– A wonderful but brief historical post reflecting on the impact of Wilberforce and the More sisters upon education today. Christian lives lived.
C.S. Lewis: A Life, by Alister McGrath – Book Review– I haven’t hard the opportunity to read this biography by Alister McGrath, but this review at least quenched some of my thirst by providing a great overview and discussion of the work.
Listening to Young Atheists: Lessons for a Stronger Christianity– What are young atheists saying? Whatever it is they are telling us about religion is quite instructive, because it allows Christians to shore up their defenses and counter the distortions atheists have about Christianity. Most importantly, it seems that Christians are viewed as insincere and unconcerned with the way their beliefs should inform their lives. Read this post and get some valuable takeaways.
Allah is not Jehovah– I found this post to be remarkably insightful. There are some who have been trying to synthesize Christianity and Islam. The fact is that these two faiths are mutually contradictory on a number of points. This post by the “Valley Girl Apologist” outlines 21 major differences between Islam and Christianity.
The Crusades: Wanton Religious Violence?
 The Crusades are often cited as the prime example of the evils of religion and of Christianity specifically. The picture is often painted of an innocent world on which Christians came in violent fervor, raping and pillaging as they went. But this picture of the Crusades is inaccurate on a number of levels. Here, I’ll explore the historical context of the Crusades with an eye towards seeing why they occurred. I’ll wrap it up with a discussion on violence and religion.
The Crusades are often cited as the prime example of the evils of religion and of Christianity specifically. The picture is often painted of an innocent world on which Christians came in violent fervor, raping and pillaging as they went. But this picture of the Crusades is inaccurate on a number of levels. Here, I’ll explore the historical context of the Crusades with an eye towards seeing why they occurred. I’ll wrap it up with a discussion on violence and religion.
The Historical Context of the Crusades
The Crusades were not just some bubbling up of violence latent within all religions. Instead, they were part of a history of conquest across the Asian and European continents. Prior to the Crusades, there was a sweeping conquest by the Muslims of territory formerly possessed by various Christian nations.
Muslim invasions had pressed in on all sides. Rodney Stark, in his extremely important work on the Crusades, God’s Battalions, notes the conquests which had pressed in on Europe from all sides. After surveying a number of Muslim conquests, he notes:
Many critics of the Crusades would seem to suppose that after the Muslims had overrun a major portion of Christendom, they should have been ignored or forgiven… This outlook is certainly unrealistic and probably insincere. Not only had the Byzantines lost most of their empire, the enemy was at their gates… (32-33)
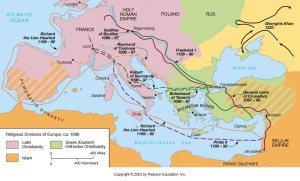
Prior to the Crusades, it is absolutely essential to note that the invaders were, quite literally, at the gates. Constantinople was threatened in the East, and Spain was overthrown in the West. Europe was under assault. The map below illustrates the situation in the time during and before the Crusades well.
The question of the Crusades must be understood within this historical setting: much of the land which European countries had controlled had been taken, by force. Furthermore, those who had taken these lands were knocking on the very gates of Europe, having already crossed into Europe in many places. Stark’s words, therefore, seem to ring true: is it really genuine to assume that these invaders should have been ignored or forgiven? Is that the reality of “secular” nations? It seems to me the very fact that so much land had been lost, as well as so much wealth, would lead many to war for “secular” reasons rather than religious reasons.
Regarding the beginning of the Crusades, Stark writes:
[T]hat’s when it all [The Crusades] started–in the seventh century, when Islamic armies swept over the larger portion of what was then Christian territory: the Middle East, Egypt, and all of North Africa, and then Spain and southern Italy, as well as many major Mediterranean islands including Sicily, Corsica, Cyprus, Rhodes, Crete, Malta, and Sardinia. (9)
So the Crusades were not unprovoked mass murders of innocents. But they were indeed quite brutal, and involved no small amount of very un-Christian activities. Raping and pillaging has no part in the Christian worldview. But Stark once again has a sobering point: war was hell. “[I]t was a brutal and intolerant age” (29). The criticism of brutality equally applies to both sides, but it is also equally anachronistic about the realities of that time. This is not to say that the horrors which occurred were not awful; it is to say that to criticize the Crusaders or Muslims as though they were doing something extraordinarily brutal for their time period is extremely short-sighted.
The Crusades as a Polemic Device
The Crusades were not all-good or all-evil affairs. Like virtually any part of human history, both good and evil intentions and outcomes were involved. To view the Crusades as either an entirely evil affair showing how religion is ultimately prone to violence or as a benevolent attempt by loving people to liberate lands that were rightfully theirs is to grossly oversimplify the historical reality. Unfortunately, modern looks at the Crusades have largely leaned towards the former of these positions, without any acknowledgement of the historical context as noted above.
Instead, the Crusades were a complex of historical events which were often brutal, often provoked, and never motivated for just one reason. To say that the Crusades are a typical example of the violence of religion is, frankly, ahistorical. Was religion involved? Yes. Were there even “religious reasons” involved in the motivations for the Crusades? Clearly. But the general movement with recent attacks on Christianity has been to argue that the Crusades were purely religious instances of religious brutality. The historical perspective provided above provides evidence against that limited perspective.
The Crusades have been used as a kind of polemic device against Christianity. Whenever it is argued that Christianity is reasonable, someone inevitably brings up this historical period. Readers will note that this historical perspective has not attempted to explain away the Crusades. Instead, I have argued for the notion that these events were historically complex, involving a number of factors beyond purely war for the sake of a faith.
As Keith Ward has noted:
It is… beyond dispute that the Crusades were a major disaster… The Crusades can be seen as justified defense… but their conduct and continuance rapidly became unjustifiable on any Christian principles. (68-69, Is Religion Dangerous?
cited below)
The point is simple: there were many motivations behind the Crusades, some of them justified. Yet in carrying out the Crusades, many horrible actions were taken which were unjustifiable. Does this somehow disprove Christianity? Not on Christianity’s own principles, on which we expect to see people acting as sinner-saints in the process of sanctification.
 Religious and Secular Violence
Religious and Secular Violence
Apart from the historical outline given here, there is another, equally important point: the dichotomy between religious violence and secular violence is simply a myth. The reason for this is because human actions are far more complex in their motivations than a simple dichotomy of one or the other reason. In our everyday experience, we know that the decisions we make are very rarely made for only one reason.
Oddly, Stark is able to note that “many historians have urged entirely material, secular explanations for the early Muslim conquests…” (13). This, in contrast to the many historians and new atheists who continue to press that the Crusades were entirely religious in their provocations. The unfortunate truth this reveals is the very human tendency to simplify history beyond the point of breaking. Human actions, particularly corporate human actions, have extremely complex motivations behind them. They are not all-or-nothing affairs which happen due to one reason or another. Very often we make decisions for a combination of reasons of differing strengths, weighing options against each other whether we realize it or not.
By utilizing the Crusades as a rhetorical device–a polemic weapon–many have done damage to the historical events themselves. Worse, they have engaged in faulty reasoning and attacked the religious other due to their own emotional hatred. The Crusades were not all-good or all-evil affairs. They were affairs of human history. To forget that is to drown them in a sea of obfuscation. Let us get beyond simple polemical attacks on the “other.” Let us instead engage in honest history and dialogue with our neighbors.
Links
The Myth of “Religion”: Constructing the Other as an enemy– I explore the notion that religion is violent and argue that one of the major difficulties with this notion is that the distinction between secular/religious is a myth.
For an interesting exploration of some aspects of Muslim Philosophy, see my book review: The Closing of the Muslim Mind.
Essential reading: Rodney Stark, God’s Battalions (New York: HarperOne, 2009).
Pacifism, Matthew 5, and “Turning the other cheek”– Glenn Andrew Peoples discusses pacifism in the Christian tradition and some of the arguments in its favor. Ultimately, he finds these arguments wanting.
Sources
Rodney Stark, God’s Battalions (New York: HarperOne, 2009).
Keith Ward, Is Religion Dangerous? (Grand Rapids, MI: Wm. B. Eerdmans, 2006).
Image Credit:
The image of the map is from this page with free resources for instructors. I do not claim credit for this image, nor do I claim that the makers of this resource in any way endorse this post.
SDG.
——
The preceding post is the property of J.W. Wartick (apart from citations, which are the property of their respective owners, and works of art as credited) and should not be reproduced in part or in whole without the expressed consent of the author. All content on this site is the property of J.W. Wartick and is made available for individual and personal usage. If you cite from these documents, whether for personal or professional purposes, please give appropriate citation with both the name of the author (J.W. Wartick) and a link to the original URL. If you’d like to repost a post, you may do so, provided you show less than half of the original post on your own site and link to the original post for the rest. You must also appropriately cite the post as noted above. This blog is protected by Creative Commons licensing. By viewing any part of this site, you are agreeing to this usage policy.
Really Recommended Posts: 11/09/2012
 I have featured literary apologetics, apologetics to Muslims and Jehovah’s Witnesses, geocreationism, and more. Check out the posts. Let me know what you liked. Come back for more.
I have featured literary apologetics, apologetics to Muslims and Jehovah’s Witnesses, geocreationism, and more. Check out the posts. Let me know what you liked. Come back for more.
Elves, Orcs, and Freaks: The Shared Authorial Vision of JRR Tolkien and Flannery O’Connor– Garret Johnson has written a very interesting look into the works of Tolkien and O’Connor. He notes that they viewed fiction as reality from a different outlook. It’s a fascinating post, and there is a second part, which can be viewed here.
An Encounter with a Jehovah’s Witness– It is easy for Christians to slam their doors on those who come door-to-door. What if, instead, we engaged them? This post is a model for engagement and provides some ways forward to engage with Jehovah’s Witnesses.
The Day After: My Thoughts on the Presidential Election– Michael Licona, author of The Resurrection of Jesus: A New Historiographical Approach, one of the best books I’ve read on the resurrection of Jesus, offers his thoughts after the election.
Human Footprints in Dinosaur Footprints– Over at GeoCreationism (a highly recommended site), Mike addresses the notion that human and dinosaur footprints have been found together or side by side. Some argue that this supports young earth creationism. Mike explores the paleontological evidence.
Meet the Multiverse– Edgar Andrews, author of what I think is the best introduction to Christian apologetics with a scientific emphasis, Who Made God?, explores the notion of the multiverse and whether it offers a challenge to the Fine Tuning argument for the existence of God. Regarding said argument, I’ve written on it in my post on the teleological argument.
Did Jesus Claim to be Divine? (Answering Islam)– I found this look at answering Muslim objections to the deity of Christ refreshing. It offers an essentially presuppositional approach, which I have found to be very useful when engaging with Muslims. Check it out.
Really Recommended Posts 10/12/12
 Another great run around the internet today. I noticed that this edition of Really Recommended Posts has a lot on Christianity and Science, Islam, and religious or activist violence. Abortion, biochemistry, the Qur’an, violence in Islam, Mitt Romney, and more are all featured. Check out the posts. If you like them, let me know.
Another great run around the internet today. I noticed that this edition of Really Recommended Posts has a lot on Christianity and Science, Islam, and religious or activist violence. Abortion, biochemistry, the Qur’an, violence in Islam, Mitt Romney, and more are all featured. Check out the posts. If you like them, let me know.
Cataloging the Historical Anachronisms in the Qur’an– Does the Qur’an potray accurately the period that it purports to describe in historical narrative? It does not seem so. Check out some of the anachronisms which crept in.
New peer-reviewed paper in Nature falsifies Darwinian junk DNA prediction– Darwinian Evolution has long used the notion of “junk DNA” as confirmation of its naturalistic processes. However, recent study has confirmed one of the predictions of the Intelligent Design movement: this supposed junk DNA would prove to be useful. I don’t claim to be a scientist at all, but I find this very intriguing. Check out the article.
Hey Atheists, Just Shut Up Please [LANGUAGE WARNING]- I found this article very interesting. An atheist discusses how people can tend to hate the “other” in their over-enthusiastic attempts to refute them. I was pleased with the article in general, but be aware that there is some strong language there. I myself have written about how religion is often used as a mechanism to hate the “religious other.”
Would a Romney presidency boost Mormonism?– Some Christians have come out saying they are afraid to vote for Romney because it would boost Mormonism. A pastor responds briefly to these claims.
Why Abolition Must be Non-Violent– The Abolish Human Abortion blog discusses why we in the pro-life movement must not resort to violence. The struggle is between worldviews, and pro-life persons cannot say they are pro-life while using violence.
Modern Muslims Who Choose the Path of Violence– Nabeel Qureshi discusses violence in Islam and the fact that Islam is not monolithic. The important thing to think about is how and when Islam turns violent. As I have emphasized elsewhere, religion and violence must be analyzed empirically, not with a mind towards demonizing the religious “other.”
Yes, the media does deliberately misrepresent and demonize creationists– Readers of my blog know I do not hold to a young-earth position. However, like Glenn Andrew Peoples I am still offended when the media blatantly misrepresents my Christian brothers and sisters. Check out this thoughtful post.
The Myth of “Religion”: Constructing the Other as an enemy
The myth of religious violence should finally be seen for what it is: an important part of the folklore of Western societies. It does not identify any facts about the world, but rather authorizes certain arrangements of power in the modern West… The myth also helps identify Others and enemies, both internal and external, who threaten the social order and who provide the requisite villains against which the nation-state is said to protect us. (William Cavanaugh, 226, cited below)
I recently discussed a phenomenal work by William Cavanaugh, The Myth of Religious Violence. It has forced me to rethink a number of issues. The fact of the matter is that although that which we generally term “religious” often may be involved in violence, the categories of “secular” and “religious” are themselves social constructs which have been used in the West to stigmatize the religious Other.
The Myth Played Out
The religious other is said to be violent. Religions cause violence due to their scary propensity to link with irrationality, absolutism, and divisive. Religion caused wars and chaos. Religious persons engaged in wars for God over nothing but minute doctrinal differences raged across the time of the reformation and at other times as well. The rise of the secular nation-state and the squelching of religion in the public square allowed for the cessation of violence and for man to live in peace. Such goes the myth of religious violence. Cavanaugh refers to this myth as a “creation myth” of the nation-state (123).
Notice the themes that run through any discussion of religion and violence. The general theme is that religion causes division through doctrinal matters. Because person A believes x and person B believes y, they argue, Furthermore, because neither x nor y has sufficient rational grounds for A and B to resolve the issue, they must fight in order to determine is right. After all, religion deals with absolutes. A and B square off about salvation–their eternal souls are at stake!
Often, religious persons are tempted to come back and counter that those who are non-religious are often violent too. However, this is itself a reaction to the same factors that drive the notion of religious violence. Namely, the myth of religious violence is used to stigmatize the Other. It constructs temporary categories of “religious” and “secular,” groups people based upon that, and then delegates the worst types of violence to that which is called religious. The myth is part of the justification for the nation-state and nationalism. The Nation is that which protects us from the Others in our own society. Without the protection of the State, we would turn to violence to try to subjugate others for our own purposes. Therefore, the State becomes a sacred object. Its symbols become cultic objects, and we ritualize specific aspects of the State. After all, the Nation is our savior from violence of religion. People will willingly lay their lives down in the name of their country, but for their religion? Certainly not! The State is worth dying for because it defends all people, but a religion is an internalized, personal object.
Thus, those things deemed religious are stigmatized and forced into the personal sphere, while those deemed secular are allowed for public debate. As such, specific aspects of a person’s worldview are forcibly separated and parsed. The religious person is expected to act “secular” when it comes to the public sphere, but is allowed to do whatever he wishes in the private realm. The problems quickly become clear.
Religion as a Myth
Religion itself is a social construct. I have seen this personally in a number of works dealing with “religion.” Rarely do authors attempt anything more than a working definition, and even then the definitions do little to outline real differences between that which is “secular” and that which is “religion.” The definitions are either extremely vague or too specific.
A survey of literature on religion shows that this problem is pervasive. The problem is with the notion of religion itself as a category that can somehow cordon off that which is secular. It may be much more useful to speak simply of ideologies or worldviews. Thus, a side-by-side comparison of differing worldviews can indeed be made. There is no fast and hard distinction between secular and religious, for such a distinction is nothing but arbitrary.
How does one define religion in such a way that Taoism, Confucianism, Christianity, Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam all somehow fit while Marxism, Communism, Nationalism, and the like do not? It seems an impossible task. Some who read my site may notice that I frequently file things under “philosophy of religion” [including this post!]. I’m not suggesting that “religion” is an entirely useless word. What I’m suggesting here is that we must admit that the category is a construction, pure and simple. When I use “religion,” I use it pragmatically to review to an arbitrarily dilineated set of worldviews. Ultimately, “philosophy of religion” is a philosophy of worldviews: putting them side by side for comparison.
By challenging the reigning paradigm of religion as a real, transcultural, category we may thus turn to the question of violence, rationality, and the like as an empirical, philosophical, and existential study. By stripping away the prejudices that come up when someone uses the word “religious” or “secular,” we may focus upon the actual data at hand. Regarding the question of violence, we can ask questions like: “In what circumstances will worldview U turn to violence?” or “Is worldview U more prone to violence than others?” As such, extremism like that of Marxism which has killed untold millions with an atheistic paradigm can be set up alongside extremism like that of Islamicism. Thus, categories outside of “religion” can be used to analyze these cases. Surely divisiveness, absolutism, and irrationality are involved in both cases? What causes them to arise? How do we slow that tide? How do we reason with the Other?
The category “religion” is a construct of the person utilizing it. As such, it can be wielded as a weapon. And, I charge, that is exactly what the category “religion” has been used for.
Controlling the Other
Those who argue that religion causes violence are, in particular, wielding the phrase as a weapon. The religious Other is irrational, violent, and to be feared. It is “us” or “them.” One can observe this in the literature. Some endorse violence against specific religions just because they assume that the myth of religious violence will apply to the view at large.
It is this kind of mentality that the construct of religion perpetuates. It is the Other which we must fear. We, who are rational, need to fear the irrational Other. The Other causes violence, they cannot be reasoned with, and they want absolutist control over society.
The key to this discussion is that the notion of a hard line between “secular” and “religious” is a social construct. The notion of religion is indeed a construction.
The myth of religion is therefore one step towards the myth of religious violence. The key is to construct a “religious other” who is irrational, divisive, and dangerous. Thus, we can feel free to stigmatize and fear this Other. We need to make sure that the Other does not threaten us, and indeed part of this may be to use violence against the Other. After all, they are incapable of reasoning and will not listen to our sound arguments. The only thing they are capable of understanding is violence, which they have used to try to subjugate us to their views.
It is in this way that the myth is used most dangerously. The religious other is a fearsome enemy, one who must be avoided and perhaps even destroyed in order to prevent one’s own destruction. By perpetuating the notion of religion as a transcultural, transhistorical, real entity distinct from that which is secular, the possibility is made to make the religious other the enemy, while glorifying those categories which one decides are not religious. It undermines the empirical study of the way violence comes about on particular worldviews.
An Alternative Way Forward
Rather than using the category of “religion” in order to stigmatize, I suggest that we instead discuss “worldviews.” In this way, all worldviews are on the same plain. Violence may arise in certain worldviews more easily than others, whether it is nationalism or a particular worldview which is deemed “religious.” It may be extremely difficult to avoid using the term “religion” so I will not even attempt to do so. The category is a construction, so it can be used as a useful fiction. Because it is indeed a temporal, cultural distinction, I can use “religion” in a meaningful sense so far as when I say it people will tend to think of Islam, Christianity, Hinduism, and the like.
However, it is just as important to focus upon all worldviews, not those which are somewhat arbitrarily deemed “religious,” when discussing truth claims. As such, it is important to avoid the secular/religious distinction and instead focus upon factual debate and discussion over the coherence of particular views. By doing so, we can advance the discussion about worldviews while avoiding the use of the myth of “religion” to stigmatize the other.
Links
Book Review: “The Myth of Religious Violence” by William T. Cavanaugh– I review the book which has led me to discuss the ways the category of religion is used to stigmatize the other and also forced me to rethink a number of issues. I highly recommend this book.
Source
William T. Cavanaugh, The Myth of Religious Violence (New York: Oxford, 2009).
SDG.
——
The preceding post is the property of J.W. Wartick (apart from citations, which are the property of their respective owners, and works of art as credited) and should not be reproduced in part or in whole without the expressed consent of the author. All content on this site is the property of J.W. Wartick and is made available for individual and personal usage. If you cite from these documents, whether for personal or professional purposes, please give appropriate citation with both the name of the author (J.W. Wartick) and a link to the original URL. If you’d like to repost a post, you may do so, provided you show less than half of the original post on your own site and link to the original post for the rest. You must also appropriately cite the post as noted above. This blog is protected by Creative Commons licensing. By viewing any part of this site, you are agreeing to this usage policy.
Really Recommended Posts 9/21/12
 There are so many fantastic posts out there it has been hard for me to keep up. I actually have another RRP scheduled with all the backlogged posts I’ve run into. Let me know which posts you’ve enjoyed. I feature here a diverse spread of posts. The necessity of apologetics, atheism, the Gospel of Barnabas (!?), young earth creationism, and resisting sin are all featured. Check ’em!
There are so many fantastic posts out there it has been hard for me to keep up. I actually have another RRP scheduled with all the backlogged posts I’ve run into. Let me know which posts you’ve enjoyed. I feature here a diverse spread of posts. The necessity of apologetics, atheism, the Gospel of Barnabas (!?), young earth creationism, and resisting sin are all featured. Check ’em!
Sarah Geis provides pointers for constructive debate and disagreement– A creative look at how to debate constructively by showing how not to do so.
Why Apologetics Should Be A Requirement For Every Pastor– Fellow Christians, I hope this post convicts you like it convicted me. We need to be doing apologetics. We owe it to our youths, we owe it to the adults in our congregations, and we owe it to ourselves.
Born Atheists?– Yes, you have heard it somewhere. We’re all born atheists. Really? What is that even supposed to mean? I found this post really excellent and it got me thinking. Check it out.
What is the Gospel of Barnabas?– Some Muslims have been claiming that the so-called Gospel of Barnabas falsifies the Christian doctrine of the Son of God. It is not, however, a serious threat. Check out this post to get some great historical information on this attempt to refute Christianity.
Atheism, Agnosticism, and the New Atheists– It never gets old. What does “atheist” mean? Don’t atheists just believe in one fewer god than believers? I’ve written about this topic myself. Check out this great post on the subject.
A Young Earth Chronometer?– One of my favorite websites has recently taken an intense three-part look at the claim that the amount of salt in the ocean is evidence for a young earth. I highly, heartily recommend the site itself to all my readers, Naturalis Historia.
How to Start a Preemptive Strike on a Sinful Inclination– Another one of my favorite and highly recommended sites, No Apologies Allowed, posted this thought-provoking comic about resisting sin.
The Presumption of Pluralism: How religious pluralism devalues all religious persons
What’s true for you is true for you, what’s true for me is true for me.
All religious backgrounds have a piece of the puzzle.
All roads lead to the same goal.
Pluralism is rampant in our society. People want to affirm everyone’s belief. Tolerance is the buzzword. Few want to talk about the differences in worldviews. It’s easier to affirm everyone’s beliefs as having a place in the interchange of ideas.
Pluralism is the position that all religions are true. This can be qualified in a number of ways. Often, the views are not well-thought out and amount to little more than saying that all ways get to heaven. However, there are thoughtful pluralists with highly developed structures for affirming their professed pluralism. For example, John Hick, a well known proponent of pluralism, writes:
[T]he Transcendent in ‘its’ inner nature is beyond human description or comprehension… it is ineffable or, as I would rather say, transcategorical, beyond the scope of our human concepts. It is to this ultimate transcategorical reality that the religions are oriented and to which they are human responses. (Hick, 163, cited below)
Thus, for Hick and most other pluralists, all religions are oriented towards some kind of Ultimate or Transcendent, from which they derive all of their beliefs. Thus, these pluralists can affirm the notion that all religions are “true” in a qualified sense.
The problem with pluralistic claims is that in their gusto to affirm all religions as true, what they’ve actually done is said that all religions are false. Again, Hick realizes a problem inherent in qualifying religions–and specifically Christianity–such that they can all be true. The problem is that some claim to have stated actual truths about transcendent reality. In other words, when a theologian claims that God is Triune, they are making a claim about objective reality. But Hick’s proposed solution is to simply place such theological claims into the reports of experiences about the “Real”: “according to our hypothesis, the different traditions are not reporting experiences of the Real in itself, but of its different manifestations within human consciousness” (171, cited below). Unfortunately for pluralists, what this has done is create what I find to be the real problem for pluralists.
The problem is that the pluralist is the only one whose claims about the Real/Transcendent are true.
The presumption of pluralism is that it assumes the invalidity of all religious claims. Only the pluralist can see that all religious claims to exclusivity are false. The exclusive claims of individual religions are dismissed offhand. After all, if all ways are true, then none can be exclusive.
Again, look at the reasoning from Hick: the claims of theologians are not actually claims about the Real itself. Rather, the claims of the theologian apply only to the Real-as-experienced in human consciousness. In other words, those making truth claims about individual religions are only expressing claims about their own subjective experience of an objective reality: the Real.
Thus, the pluralist undermines the truth claims of all religions, while simultaneously trying to affirm them. Only the pluralist is able to look beyond the truth claims of religion and see that when the Muslim claims that Allah is the only God, he is mistakenly reporting his experience as opposed to a claim about reality. Only the pluralist can see that the Christian who claims that Jesus is the only savior, she is only reporting her conscious experience of the Real. The Buddhist who says there is no God is similarly mistaken: perhaps there is? Who knows? Only the pluralist can see that all of these contradictory claims about religious reality are in fact merely the reports of conscious experience of a supra-reality: one which stands above all religions and is the true religion.
The bottom line is that the pluralist has become the exclusivist. Only the pluralist knows the true way. Thus, their system must collapse in on itself. It either relegates all religious claims to become mere reports of human consciousness and thus affirms itself as the only true religion, or it must affirm blatantly contradictory claims like “God exists” and “There is no God” or “Shiva is a god, Vishnu is a god, etc.” and “There is no God but Allah.” The pluralist has presumed much.
If all ways are true, then none are. Pluralism has failed.
Links
Can we evaluate worldviews?– I discuss how to evaluate rival worldviews and outline some criteria by which to do it.
A Vision for Christian Apologetics to World Religions– I outline a vision for Christians interacting with believers of other faiths. Integral to this approach is understanding others’ beliefs.
Source
John Hick, The New Frontier of Science and Religion (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010).
SDG.
——
The preceding post is the property of J.W. Wartick (apart from citations, which are the property of their respective owners, and works of art as credited) and should not be reproduced in part or in whole without the expressed consent of the author. All content on this site is the property of J.W. Wartick and is made available for individual and personal usage. If you cite from these documents, whether for personal or professional purposes, please give appropriate citation with both the name of the author (J.W. Wartick) and a link to the original URL. If you’d like to repost a post, you may do so, provided you show less than half of the original post on your own site and link to the original post for the rest. You must also appropriately cite the post as noted above. This blog is protected by Creative Commons licensing. By viewing any part of this site, you are agreeing to this usage policy.
Book Review: “The Myth of Religious Violence” by William Cavanaugh
 William T. Cavanaugh’s The Myth of Religious Violence
William T. Cavanaugh’s The Myth of Religious Violence (hereafter MRV) examines the oft-perpetuated notion that religion causes violence. Cavanaugh levels an attack against this notion that comes in two primary directions: 1) He argues that “ideologies and institutions labeled ‘secular’ can be just as violent as those labeled ‘religious'”; 2) He argues that the “twin categories of religious and secular” are constructs which are used to “provide secular social orders with a stock character, the religious fanatic, to serve as enemy” (3-5).
Violence in the name of…
Cavanaugh first turns to the analysis of violence. He argues that rather than just declaring “religion” violent, people should engage in an empirical study. In analyzing various “ideologies, practices, and institutions” like “Islam, Marxism, capitalism, Christianity, nationalism, Confucianism, secularism, Hinduism…” “A careful examination of the varieties of each [worldview] and the empirical conditions under which each does in fact support violence is helpful and necessary. What is not helpful is to divide the above list into religious and secular phenomena and then claim that the former are more prone to violence… such a division is arbitrary and unsustainable on either theoretical or empirical grounds” (16).
Next, Cavanaugh analyzes three ways that religion is supposed to be tied intrinsically to violence. These are that “religion causes violence because it is (1) absolutist, (2) divisive, and (3) insufficiently rational” (17-18). MRV follows several important thinkers who argue from each camp. Cavanaugh concludes that:
[T]here is no doubt that, under certain circumstances, particular construals of Islam or Christianity contribute to violence… Where the above arguments [about the intrinsic ties of religion to violence]–and others like them–fail is in trying to separate a category called religion with a peculiar tendency toward violence from a putatively secular reality that is less prone to violence. There is no reason to suppose that so-called secular ideologies such as nationalism, patriotism, capitalism, Marxism, and liberalism are any less prone to be absolutist, divisive, and irrational than belief in, for example, the biblical God (54-55).
The Myth of Religion
In a very real sense, MRV could just as easily be titled The Myth of Religion. Cavanaugh argues extensively for the conclusion that “Within the west, religion was invented as a transhistorical and transcultural impulse embedded in the human heart, essentially distinct from the public business of government and economic life” (120).
The attempt to define “religion” has “nothing close to agreement among scholars…” (57). In fact, “[t]here is a significant and growing body of scholars… who have been exploring the ways that the very category religion has been constructed in different times and different places… Religion is a constructed category, not a neutral descriptor of a reality that is simply out there in the world” (58). Following Jonathan Z. Smith, Cavanaugh states, “religion is not simply found, but invented. The term religion has been used in different times and places by different people according to different interests” (58).
Cavanaugh argues towards these conclusion through multiple lines of evidence. First, the concept of religion itself is different across different times and places. The Western notion of religion is not mirrored in other cultures (61). Yet even in the west, the concept of what denoted “religion” evolved. The concept was used simply to mean “worship” in the past (63). Through the medieval period, religion basically just meant “rites” or “piety”: religion was “not a universal genus of which Christianity is a particular species” (64-65).
Thus, religion was “invented in the West.” Now it has come to mean a “universal genus of which the various religions are species” (69). Part of this development was due to a need in the Reformation to demarcate differences between the varying schools of thought (72ff). When moderns use the concept religion in a universal fashion, such as Edward, Lord Herbert of Cherbury (1583-1648) did, the problem “is that it is unfalsifiable. In constructing an a priori religion in the minds of all people, Herbert [and those like him] has made his theory impervious to empirical evidence. All evidence is seen and interpreted through the lens of his religious view a priori” (77). “There was a time when religion, as modern people use the term, was not, and then it was invented” (81).
MRV then outlines two ways to define religion, either through a substantavist–one which focuses on the content of religion–or functionalist–which focuses on how a practice functions–approach. The problem with a substantivist definition is that “even if one were able to come up with a coherent, transhistorical, and transcultural definition of religion which would include things like Christianity and Confucianism and Buddhism and exclude things like Marxism and nationalism and capitalism, it would not tell us anything worthwhile about the cuases of violence. Indeed, to exclude [the latter three] a priori from an investigation of violence in the service of ideology in fact distorts the results of any such study” (105). Functionalist definitions fare slightly better because they define religion in such a way that “‘if it looks like a religion and acts like a religion, then it is a religion'” (109). This approach is capable of including things like the American Civil Religion.
Thus, Cavanaugh states that “there is no transhistorical or transcultural concept of religion. Religion has a history, and what counts as religion and what does not in any given context depends on different configurations of power and authority… the attempt to say that there is a transhistorical and transcultural concept of religion that is separable from secular phenomena is itself part of a particular configuration of power, that of the modern, liberal nation-state as it developed in the West (59).
What does this mean for violence and religion? Cavanaugh proposes a test:
The crucial test, however, is what people do with their bodies. It is clear that, among those who identify themselves as Christians in the United States, there are very few who would be willing to kill in the name of the Christian God, whereas the willingness, under certain circumstances, to kill and die for the nation in war is generally taken for granted (122).
The Creation Myth of the Wars of Religion
The story goes that, after the Protestant Reformation divided Christendom along religious lines, Catholics and Protestants began killing each other for holding to different doctrines. The wars of religion… demonstrated to the West the inherent danger of public religion. The solution to the problem lay in the rise of the modern state, in which religious loyalties were marginalized and the state secured a monopoly on the means of violence…
This story is more than just a prominent example of the myth of religious violence. It has a foundational importance for the secular West, because it explains the origin of its way of life and its system of governance. It is a creation myth for modernity (123).
Following the lines of thinking of Voltaire, John Locke, and others, Cavanaugh argues that the myth of religious violence is perpetuated in order to marginalize that which is considered religious and give rise to the nation-state. According to this myth, “All theological religions are to be tolerated, provided they do not interfere with the obligations of citizens to the state…” (129). The myth is that religion is divisive and that they “fight over doctrines or ‘religious creeds'” so that “the state steps in to make peace” (130).
Cavanaugh shows that this myth is indeed false. The “wars of religion” had any number of motivating factors. The use of this story is not so much to tell a truth as it is a means by which to legitimize the nation-state. He argues towards these conclusions by showing that many “wars of religion” were in fact wars of economy, wars of power structures, and the like. He notes four primary factors for this myth to work: that combatants were motivated by religious difference, that the primary cause of war was religion, that religious causes are analytically separable from political, economic, and social causes at the time of the wars, and that the rise of the modern state was not a cause of the wars (141-142). He then analyzes each of these in turn based upon the historical record and shows that these all fail to account for the actual history of the “wars of religion.” In fact, the opposite is true in each case (142-177).
“We must conclude that the myth of the wars of religion is finally incredible, which is to say, false” (177).
The Uses of the Myth
Perhaps the most challenging and paradigm-shifting portion of the book is that which focuses upon the uses of the myth of religious violence. Cavanaugh argues that the myth is so perpetuated because of its usefulness.
First, he analyzes the use of the myth in building the “wall of separation” between church and state. He examines a number of supreme courses and how the myth of religious violence was used to favor the constructed notion of “secular” over that of “religious” (183ff).
The myth of religious violence is used to create a religious “other” which can then be exploited, coerced, and denigrated. “[R]eligion–or more precisely, religion in public–is what the liberal nation-state saves us from” (192). History is revised in order to show how religion is that which causes violence, while the secular nation-state is that toward which we should turn for salvation.
Oddly, it is permitted, encouraged, and sometimes even required to give devotion to the nation state, while this is not religious. “We are all Americans, and devotional exercises [the pledge of allegiance, venerating of the flag, etc.] meant to instill love of our country are unitive, not divisive. Such exercises, however, are not religion. Patriotism, in this world view, is defined over against public religion. To allow that patriotism might be a type of religion and might carry its own dangers of violence would threaten the very basis of our social order” (192).
On a functionalist definition of religion, however, nationalism counts as religion. “American religion” has “saints (the founding fathers)… shrines (Independence Hall)… relics (the Liberty Bell)… holy scriptures (the Declaration of Independence, the Constitution)… martyrs (Lincoln)… inquisition (school boards that enforce patriotism)…” and various religious festivals (Flag Day, the Fourth of July) (117). Nationalism is prevalent in many countries. Religion is privatized, secular nationalism is standardized and enforced. Not only that, but “Only the nation-state may kill” (118).
Again, Cavanaugh’s point ties into his earlier discussion: the ties to violence must be an empirical study based upon ideologies, not one based upon constructed categories of religious and secular. These categories are faulty in-and-of themselves. Furthermore, they undermine the possibility of the empirical study of violence. Nationalism and secularism–ideologies in other words–can be every bit as violent as some ideologies called “religion.”
The myth is also used to hide possible “secular” causes for war. Al Qaeda is specifically religious, and the West is all too happy to use this to ignore the fact that its own mistakes in installing regimes in the Middle East has caused the rise of absolutist, controlling states (202ff).
Worst of all, the myth of religious violence has been used to carry out violence against the religious other. Those who perpetuate this myth often use it in order to legitimize violence against the religious person, who, after all, is irrational and incapable of reason due to their religious beliefs. Sam Harris is a prime example of this notion. He argues that “There are other ideologies with which to expunge the last vapors of reasonableness from a society’s discourse, but Islam is undoubtedly one of the best we’ve got” (HarrisThe End of Faith, 136, quoted in Cavanaugh, 214). Furthermore, “Some propositions are so dangerous that it may even be ethical to kill people for believing them… Certain beliefs place their adherents beyond the reach of peaceful means of persuasion while inspiring them to commit acts of extraordinary violence against others” (Ibid, 52-53, quoted in MRV 213). Notice how this works: the religious other is that which is unreasonable and violent; in order to stop their violence, it may be ethical to kill them for their beliefs. Harris is not the only one who perpetuates this ideology. Cavanaugh cites a number of other thinkers who have utilized the myth of religious violence in this fashion.
Killing for religion is bad, killing for the state is often good (219). As Cavanaugh states, “The myth of religious violence thus becomes a justification for the use of violence. We will have peace once we have bombed the Muslims into being reasonable” (215). This analysis of violence again plays off the myth of religious violence: “Violence labeled religious is always irrational, particularly virulent, and reprehensible. Violence labeled secular, on the other hand, no matter how regrettable, is often necessary and sometimes even praiseworthy for the job it does defending us from religious violence” (216).
Violence feeds on the need for enemies, the need to separate us from them. Such binary ways of dividing the world make the world understandable for us, but they also make the world unlivable for many. Doing away with the myth of religious violence is one way of resisting such binaries, and, perhaps, turning some enemies into friends (230).
Conclusion
It is rare that one comes across a book that forces them to rethink just about everything they have thought about a specific issue. William Cavanaugh’s The Myth of Religious Violence is one of those books which will challenge readers on every level of the discussion. It has an extremely broad scope, but argues convincingly and with a depth that seems almost indefeasible.
The myth of religious suffers a number of serious defects. It assumes an unwarranted division between the constructed categories of “religious” and “secular,” it oversimplifies the justification for violence, it is a clear example of a creation myth used for the founding of the nation state, and most alarmingly it is used to justify violence against the religious other.
The myth of religious violence may live on on the popular level, but Cavanaugh has dealt its death blow. Whether it takes 50 years or never happens, the myth has been destroyed.
The review has been lengthy, but that is due to the importance of this topic. I will be expanding on and elaborating Cavanaugh’s ideas over the course of the next 1-2 months. Check back here, where I will post links to future posts, or be sure to follow the blog to catch the posts over the coming weeks.
Finally, I want to say that this book was a gift from an anonymous donor from this site and I must say Thank you, you have been a huge blessing! It was so delightful to receive a book out of the blue, and to have it be so fantastic was another reward.
Source
William T. Cavanaugh, The Myth of Religious Violence (New York: Oxford, 2009).
SDG.
——
The preceding post is the property of J.W. Wartick (apart from citations, which are the property of their respective owners, and works of art as credited) and should not be reproduced in part or in whole without the expressed consent of the author. All content on this site is the property of J.W. Wartick and is made available for individual and personal usage. If you cite from these documents, whether for personal or professional purposes, please give appropriate citation with both the name of the author (J.W. Wartick) and a link to the original URL. If you’d like to repost a post, you may do so, provided you show less than half of the original post on your own site and link to the original post for the rest. You must also appropriately cite the post as noted above. This blog is protected by Creative Commons licensing. By viewing any part of this site, you are agreeing to this usage policy.
Really Recommended Posts 9/1/12
 I am constantly delighted by the great quality of posts by my brothers and sisters in Christ. This week, I have provided a choice selection. The topics range from politics (the doctrine of peace through strength) to young earth creationism to presuppositional apologetics and Islam and beyond. I even linked to three of my favorite songs, to give a slightly different feel this go-round.
I am constantly delighted by the great quality of posts by my brothers and sisters in Christ. This week, I have provided a choice selection. The topics range from politics (the doctrine of peace through strength) to young earth creationism to presuppositional apologetics and Islam and beyond. I even linked to three of my favorite songs, to give a slightly different feel this go-round.
As always, please let me know what you liked!
———
The Natural Historian writes about Isaac Newton’s thoughts on the Mosaic account of creation. Check out this excellent quote:
Attempts to bring explanations for the physical origins of the geographic features of the earth into conformity with a six day creation and a universal flood has never yielded a unified view of how to interpret the data… [T]he application of that traditional view [young earth creationism] to an understanding of the physical creation and the origin of the earth has never accomplished a satisfying nor widely accepted result.
Refuting Islam: Philosophical Analysis– Mike Robinson uses presuppositional apologetics to evaluate Islam and argues that Islam is founded upon a logical fallacy.
Of Jesus, the Woman Caught in Adultery, Public Morality, The Law…– A fantastic and lengthy post on Christianity in the public square, legislating morality, and some specific moral issues. Recommended if you enjoy political discussion and the interaction of faith with politics.
What is the Doctrine of Peace Through Strength?– Wintery Knight weighs in on a national defense policy of peace through strength. This isn’t directly related to Christian apologetics, but I found it interesting, and Wintery Knight is a master of discussing Christianity in the public square. Check out the rest of his site. A choice quote from the article on peace through strength:
The way to stop most wars is to make dictators believe that you have the means and the will to stop their aggression.
The Ring Makes All the Difference: A Word to the Wise on Cohabitation– Does marriage make a difference? Should we do trial runs of living together first? What does sociology say about these issues? Check out this informative article.
Some of My Favorite Music– Here are some links to songs by three of my favorite artists. Yes, they range wildly in genre. I like some Christian rap- like Lecrae; I like Christian Metal like Demon Hunter (my favorite band) and I love some Christian Blues too, check out the Glenn Kaiser Band.